EV Charging Infrastructure: USA vs India — Who’s Winning?
This comparison of EV charging infrastructure USA vs India breaks down network growth, policy support, and real-world accessibility—revealing which country is truly leading the race toward an electric future.

Introduction
EV charging infrastructure has become the backbone of electric mobility. The ev charging infrastructure in the USA has surged in scale, while India is racing to catch up—but the paths differ drastically.
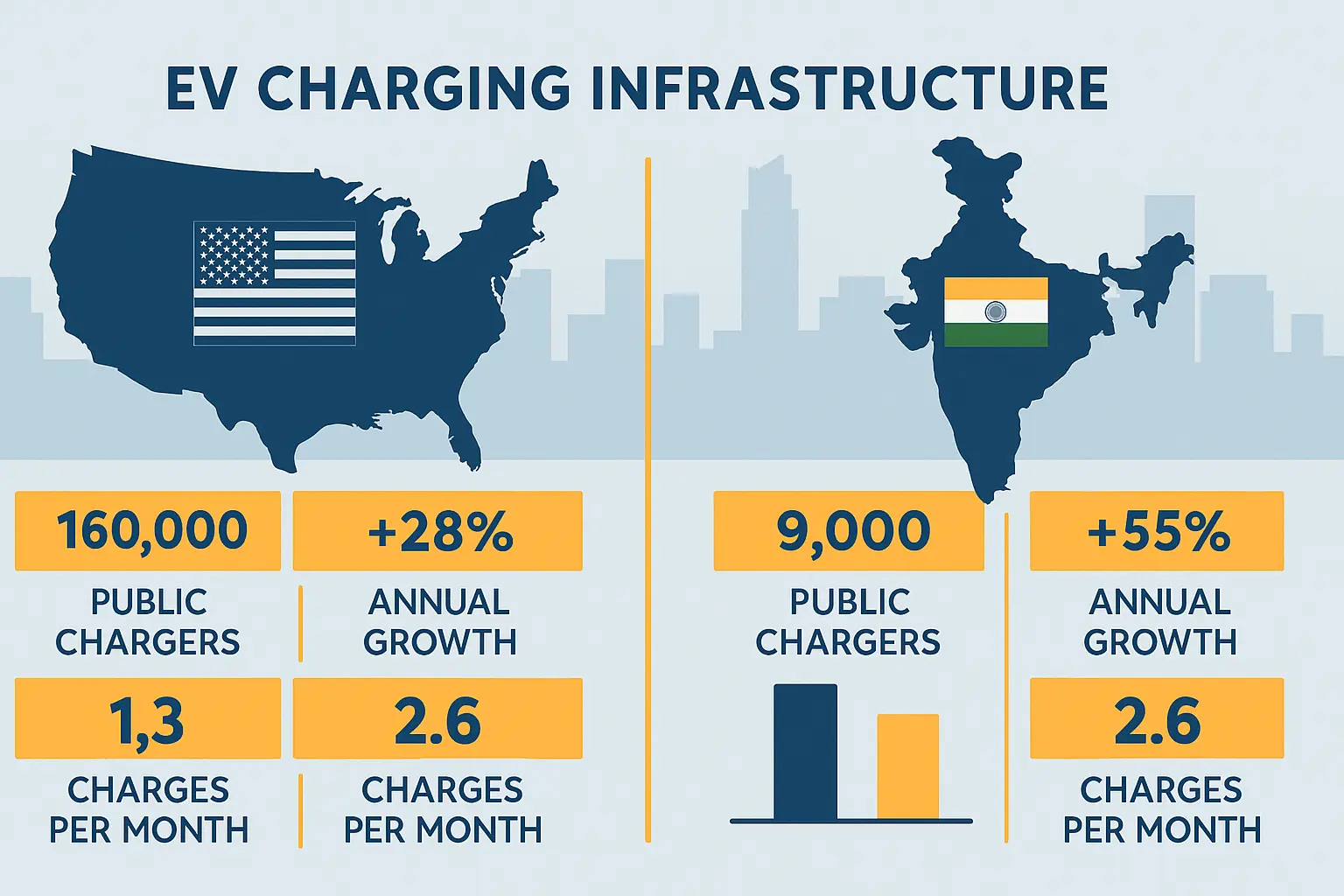
With over 60,000 fast-charging ports now reported in the U.S. (an 80% rise in two years) Wall Street Journal, and India’s public chargers growing fivefold in three years , the contrast is dramatic.
Which country leads, which lags, and what can each learn from the other?
Quick Summary:
- U.S. has scale, reliability, and dense coverage; India shows rapid percentage growth but base is low.
- Policy, grid readiness, and business models are key differentiators.
- Future growth depends on interoperability, standards, and investment.

What Is EV Charging Infrastructure?
EV charging infrastructure refers to the network of stations, connectors, and supporting systems that allow electric vehicles to recharge.
- Public charging stations (Level 2 AC, DC fast charging)
- Home and workplace chargers
- Grid & energy management systems
- Software layers (apps for locating, payments, reliability)
In comparing the U.S. and India, we analyze quantity, quality, accessibility, business models, and policy support.

$500 Walmart Gift Card
Some users qualify for a $500 Walmart gift card. You can check if you qualify.
Why It Matters
- Range anxiety mitigation: Charging access is essential for EV adoption.
- Grid impact & load management: Poor infrastructure can cause strain.
- Economic and environmental goals: EVs help decarbonize transport; charging infrastructure enables that.
- Market competitiveness: Countries that lead in infrastructure can attract EV manufacturing, innovation.
How USA and India Differ: Key Dimensions
Capacity & Scale
- In the U.S., 64% of Americans live within 2 miles of a public EV charger.
- Electrify America operates over 950 stations with 4,250+ DC fast connectors .
- India’s market size was USD 443.3 million in 2024 for charging infrastructure, expected to grow to USD 1,901 million by 2030 (CAGR ~27.8%) .
- Yet India still has just one public charger for every 235 EVs as of early 2025 .
Growth & Trajectory
- India’s public charging count jumped from ~5,151 (2022) to ~26,367 (2025) — fivefold growth.
- Globally, EV charging infrastructure (public + private) is projected to reach USD 125.4 billion by 2030, up from $32.3B in 2024.
Reliability & Downtime
- A study of 657 DC fast chargers in California found 72.5% functionality on spot check; issues included broken screens and payment failures.
- U.S. networks are under pressure to maintain uptime, especially given expectations of reliability.
Interoperability & Standards
- U.S. uses standards like SAE J1772, CCS, and NACS connectors.
- India adopts Bharat AC-001 / DC standards (IS 17017) in alignment with IEC standards for compatibility.
- Interoperability across networks and app layers is a bigger challenge in India due to diverse states and operators.
Policy & Incentives
- U.S. federal and state funding drives charger deployment, though some programs have underdelivered; as of April 2025, under $7.5B programs, fewer than 400 ports built.
- In India, central and state schemes like PM E-DRIVE (USD ~240 million allocation) support charging rollout.
- Tata Motors plans to double charging points to 400,000 over next two years in India.
Which Side Leads — and Why?
U.S. Strengths
- Larger base: has built scale earlier, more capital & infrastructure readiness.
- Better grid and supporting energy systems.
- Private sector participation (e.g., Electrify America) with strong backing.
India Strengths & Momentum
- Fast percentage growth, lower base makes leaps possible.
- Government push and subsidies.
- Modular charging strategies (e.g., public, workplace, highway).
Challenges India Must Solve
- Ensuring charger-to-EV ratio improves (currently ~235 EVs per charger).
- Standardization across states.
- Reliability, maintenance, and uptime of charging stations.
How to Build Better EV Charging Infrastructure
- Adopt unified standards for connectors, payment systems, and communication protocols.
- Encourage private-public partnerships — share risk and investment.
- Deploy at multi-tier locations: homes, workplaces, highways, malls.
- Build redundancy & maintenance plans — uptime is critical.
- Smart grid & renewable integration to manage load and green charging.
- Subsidies and incentives tied to performance (uptime, coverage).
- Consumer apps & mapping tools to ease discovery and usability.
Common Myths & Misconceptions
- Myth: India is behind beyond catch-up.
While behind in scale, India’s high growth suggests fast closing in. - Myth: More chargers always means better performance.
Not unless reliability, distribution, and maintenance are good. - Mistake: Investing only in fast chargers.
Slower AC chargers in everyday spots matter too. - Myth: EV charging is just infrastructure, not tech.
Smart software, payments, analytics are core differentiators.
Expert Views, Reports & Case Studies
- IEA’s Global EV Outlook 2025 highlights the essential role of charging infrastructure growth worldwide.
- U.S. public access data shows ~64% Americans live within 2 miles of a charger, influencing EV adoption sentiment.
- Electrify America’s expansion to 950 stations demonstrates scalability of private networks.
- In India, NITI’s official report states ~2,636 public chargers sanctioned in 62 cities across 24 states/UTs.
- Case: Tata’s plan to double India’s charging points to 400,000 in next two years demonstrates ambition.

$750 Cash App Gift Card
Some users qualify for a $750 Cash App gift card. You can check if you qualify.
FAQs
Q: What is ev charging infrastructure?
It includes public and private charging stations, grid systems, software, and standards enabling EV recharging.
Q: Who has better EV charging infrastructure — USA or India?
The U.S. leads in scale, reliability, and density; India leads in growth rate and future potential.
Q: How fast is India’s EV charging growth?
India’s public chargers grew fivefold in three years; yet still only ~1 charger per 235 EVs.
Q: What are the major challenges for EV charging in India?
Standards, reliability, interstate coordination, grid strength, and financing.
Q: Can U.S. and India learn from each other’s models?
Yes — U.S. can learn agility and scale deployment from India’s momentum; India can learn reliability and standards from U.S. systems.
Key Takeaways
- Ev charging infrastructure in the U.S. exhibits maturity, dense coverage, and reliability, while India’s infrastructure is rapidly scaling from a low base.
- Policy support, private investment, and smart planning are pivotal in both countries.
- Interoperability, uptime, and standards determine real usability—not just the number of chargers.
- India’s rapid growth trajectory is promising, but reliability and distribution will define success.
- A hybrid model combining public, private, and community chargers, backed by strong tech and finance, will shape future infrastructure globally.
Conclusion
Comparing EV charging infrastructure in the U.S. and India reveals both contrasts and converging paths. The U.S. leads on scale and reliability; India leads in growth rate and policy momentum.
Their journeys teach us: scale must be supported by reliability, standards, and consumer trust. As both nations advance, their models may merge—unlocking a global blueprint for electric mobility infrastructure.




