India’s Gen Z Money Habits: A Wealth Lesson for America
This analysis of India’s Gen Z money habits uncovers the saving, investing, and digital-first strategies shaping a financially smarter generation—revealing powerful lessons America can use to build long-term wealth.

Introduction
Financial Literacy Secrets lessons India hold surprising relevance for Indians and immigrants in the USA. While the U.S. boasts robust financial markets, India’s youth have shown strikingly disciplined money habits, especially through digital finance and saving culture.
In India, only about 27% of the population is financially literate, and youth literacy is even lower—with many unaware of basics like investment, credit, or compounding. Yet, despite the gaps, many young Indians practice disciplined saving, use digital tools, and invest early.
What if those lessons—adapted smartly—became a secret edge for building wealth in the U.S.?
Quick Summary:
- Indian youth emphasize disciplined saving, small investments, and digital-first finance.
- Key lessons: start small, automate, diversify, lean into community education.
- In the U.S., these habits translate into stronger financial health, better investment outcomes, and resilience.

$750 Cash App Gift Card
Some users qualify for a $750 Cash App gift card. You can check if you qualify.
What Do We Mean by “Financial Literacy Lessons from India’s Youth”?
By “financial literacy lessons India’s youth”, we refer to money management, saving, investment, and mindset behaviors practiced by young Indians that stem from cultural, social, and economic constraints. These include:
- Habitual saving (no matter how small)
- Using digital tools and micro-investment platforms
- Prioritizing low-cost, systematic instruments
- Community or peer learning in fintech spaces
When we speak of applying these in the USA, it means adapting those behaviors into U.S. financial ecosystems—IRAs, 401(k)s, stocks, real estate—while respecting differences in regulation, tax, and opportunity.
Why These Lessons Matter for Building Wealth in the USA
- Behavior first, tools second: Good habits transfer across geographies more easily than product knowledge.
- Bridging cultural advantage: Many Indians already bring saving discipline; with proper financial literacy adjusted for U.S., the leverage is high.
- Digital finance synergy: Indian youth are fluent in fintech—integrating with U.S. platforms is natural.
- Underused potential: Many immigrants underutilize wealth-building tools in U.S. out of unfamiliarity. India’s youth lessons help bridge that gap.
Core Lessons & Habits from Indian Youth That Translate to U.S. Wealth Building
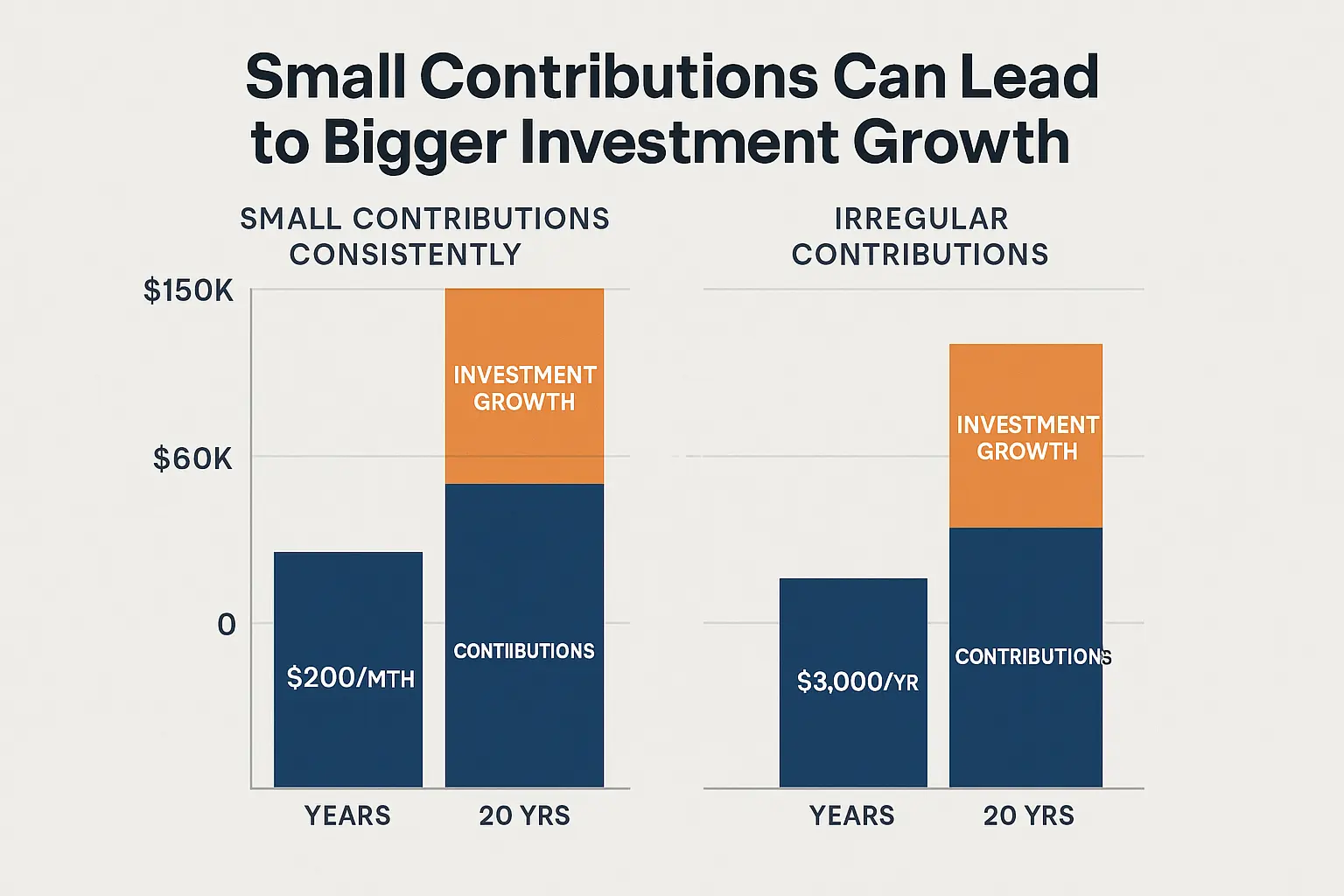
1. Start Small, Be Consistent
Many Indian youth invest ₹100–₹500 monthly via SIPs (Systematic Investment Plans). Even though markets in India are volatile, the habit is powerful.
U.S. Application:
- Automate small contributions to Roth IRA, ETFs, or brokerage
- Use fractional share investing platforms (e.g., M1 Finance, Schwab fractional)
2. Automate & Make It Invisible
Indian apps often offer auto-debit for SIPs and recurring plans. This reduces human friction.
U.S. Application:
- Set up automatic payroll or bank transfers to retirement, investment, and emergency accounts
- Use “round-up” investing apps (e.g., Acorns)
3. Embrace Low-Cost, Diversified Instruments
In India, equity mutual funds, index funds, and ETFs are common picks for youth investors.
U.S. Application:
- Favor low-cost index funds / ETFs
- Avoid high-fee products
- Diversify globally
4. Use Digital First & Community Learning
Indian youth consume finance content via YouTube, Telegram, WhatsApp groups. They share tips, memes, micro-courses.
U.S. Application:
- Join communities (e.g., r/personal finance, Indian diaspora investing groups)
- Use online courses and micro-learning apps
5. Leverage Social Accountability & Peer Pressure
In India, seeing peers invest or share “portfolio updates” encourages action. Social validation becomes a motivator.
U.S. Application:
- Share goals with friends or spouses
- Use group challenges (e.g. “no-spend month,” savings sprints)
Adapting Lessons to U.S. Realities (Best Practices)
- Understand tax-advantaged accounts
Learn Roth IRA, 401(k) matching, HSA, and their benefits. - Build emergency fund first
Save 3–6 months of expense before investing heavily. - Balance risk with time horizon
Younger years: more equities; mid-career: tilt to bonds / diversification. - Stay disciplined during market volatility
Resist panic. Indian SIP investors already lean into this. - Use U.S. financial literacy resources
CFP resources, FINRA, AARP guides. - Track progress and iterate
Review portfolio quarterly; rebalance as required.
Common Mistakes or Myths
- Myth: Indian habits don’t work in U.S. – They can, with adaptation.
- Mistake: “If small, it’s negligible.” – Compounding makes small contributions powerful.
- Myth: Digital content is enough. – Practice matters more than passive learning.
- Mistake: Not adjusting for inflows/outflows. – Income, taxes, and cost of living vary.
Expert Views, Reports & Case Studies
- A study of 400 Indian youth aged 18–30 found 61% of high-literacy individuals used SIPs versus 24% low-literacy peers. Advances in Consumer Research
- The World Economic Forum reports that only ~27% of Indian adults are financially literate—a gap that financial education initiatives aim to close. World Economic Forum
- OECD / Lusardi et al. have long correlated financial literacy with retirement planning, better debt management, and investment participation (U.S. studies) ResearchGate
- Case: An NRI in Seattle who grew up in India says his habit of saving a fixed percentage monthly helped him rapidly build a U.S. investment portfolio—even when starting afresh in a new market.

$750 Amazon Gift Card
Some users qualify for a $750 Amazon gift card. You can check if you qualify.
FAQs
Q: What are financial literacy lessons India youth teach for U.S. wealth building?
Lessons include starting small, automating contributions, using low-cost instruments, peer accountability, and digital community learning.
Q: Do those Indian youth habits work in the U.S.?
Yes—especially disciplined saving, automation, and community reinforcement—but must be adapted to U.S. tax and investment systems.
Q: Why is Indian youth financial literacy valuable for U.S. investors?
Because those habits instill consistency and behavior first—critical for long-term compounding in any market.
Q: Can someone switch late and still benefit?
Absolutely. The earlier the better—but behaviors like automation and low-cost investing work at any age.
Key Takeaways
- Financial literacy lessons India from youth—like saving small, automation, and community learning—translate well into U.S. wealth building.
- Discipline, low-cost instruments, and peer reinforcement are more powerful than strategies alone.
- Adapting for U.S. systems (tax, accounts, investment vehicles) is essential.
- Digital communities and shared accountability help maintain momentum.
- These lessons help immigrants and new U.S. earners build resilient long-term wealth.
Conclusion
Financial wisdom often comes not from complex models, but from simple habits, lived over time. The financial literacy lessons India’s youth practice—saving small, automating, diversifying, and learning in community—are powerful tools for building wealth in any market, including the U.S.
If you’re an Indian or immigrant in the U.S., carry these habits with you, adapt to new systems, and let consistency be your greatest advantage.




